Virtual Animated Media with Local Wisdom for Learning to Read using Mind Method
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.22219/kembara.v10i2.35404Keywords:
Animation, Local wisdom, Mind mapping, Reading comprehensionAbstract
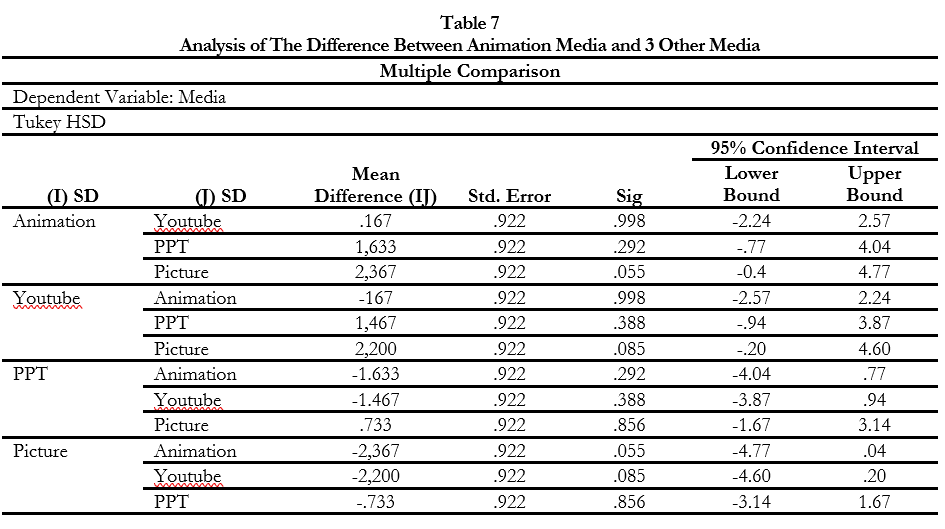
The objectives of the research are to: 1) explain the conditions of class 4 elementary schools in Madiun City; 2) describe and explain the model for developing virtual animation media containing local wisdom for learning to read for grade 4 students; 3) describe and explain the effectiveness of virtual animation media products containing local wisdom for learning to read through the Mind Mapping method for grade 4 elementary school students. This type of development research useD the simplified Borg and Gall method in 4 stages: exploration, design development, testing, and deployment. Data analysis was done using descriptive analysis, feasibility tests with criteria scores, and reading comprehension tests with t-tests. Results of the research were: 1) students still use thematic book media. Learning to read was still a task of answering questions. 2) the needs and characteristics of learning media were summarized as follows, (a) attractive animated media according to basic competencies in the curriculum, with local wisdom content (b) easy to use, (c) equipped with evaluations to measure students' reading comprehension. 3) the test results were categorized as good and feasible. (4) Media effectiveness showed a value of 0.29 greater than 0.05. The homogeneity test at the extensive test stage received a value of 0.109 which indicated significance, and the normality test with a value of 0.622 which means the population had homogeneous variance. The results of the Tukey test showed differences between the experimental and control groups. Virtual animation media is effective in reading comprehension through the mind mapping method for grade 4 students.
Downloads
References
Abrams, S. S., & Merchant, G. (2013). The digital challenge. International Handbook of Research on Children’s Literacy, Learning, and Culture, 319–332. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781118323342.ch23
Arndt, P. A. (2016). Computer usage for learning how to read and write in primary school. Trends in Neuroscience and Education, 5(3), 90–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tine.2016.07.003
Barak, M., & Dori, Y. J. (2011). Science education in primary schools: is an animation worth a thousand pictures? Journal of Science Education and Technology, 20, 608–620.
Batool, S. H., & Webber, S. (2019). Mapping the state of information literacy education in primary schools: The case of Pakistan. Library and Information Science Research, 41(2), 123–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lisr.2019.04.006
Beauty, M., Rahmawati, L. E., Markhamah, M., & Tawandorloh, K.-A. (2023). Evaluasi CIPP pembelajaran keterampilan membaca di Program Studi Pendidikan Bahasa dan Sastra Indonesia: Analisis proses dan produk. KEMBARA: Jurnal Keilmuan Bahasa, Sastra, dan Pengajarannya, 9(1), 1–14. https://doi.org/10.22219/kembara.v9i1.23516
Borg, W. R., & Gall, M. D. (1983). Educational Research. An Introduction. New York: Longman Inc.
Cheng, K. H., & Tsai, C. C. (2014). Children and parents’ reading of an augmented reality picture book: Analyses of behavioral patterns and cognitive attainment. Computers and Education, 72, 302–312. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2013.12.003
Christie, F. (1995). Pedagogic discourse in the primary school. Linguistics and Education, 7(3), 221–242. https://doi.org/10.1016/0898-5898(95)90024-1
Díaz, L. A., & Entonado, F. B. (2009). Are the functions of teachers in e-learning and face-to-face learning environments really different? Journal of Educational Technology & Society, 12(4), 331–343.
Dickinson, D. K., & Tabors, P. O. (2001). Beginning literacy with language: Young children learning at home and school. Paul H Brookes Publishing.
Diergarten, A. K., Möckel, T., Nieding, G., & Ohler, P. (2017). The impact of media literacy on children’s learning from films and hypermedia. Journal of Applied Developmental Psychology, 48, 33–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.appdev.2016.11.007
Fauzan, Setiawan, A., Musaffak, & Yufarlina Rosita, F. (2022). Pola penelitian membaca cepat dan implikasinya terhadap keterampilan membaca cepat bagi calon guru Bahasa Indonesia: Tinjauan pustaka sistematis. KEMBARA: Jurnal Keilmuan Bahasa, Sastra, dan Pengajarannya, 8(2), 436–457. https://doi.org/10.22219/kembara.v8i2.22719
Godman, K. (1996). Ken Goodman On Reading. Heinemann. Portsmouth. NH.
Gough, P. B., & Tunmer, W. E. (1986). Decoding, reading, and reading disability. Remedial and Special Education, 7(1), 6–10. https://doi.org/10.1177/074193258600700104
Guthrie, J. T., Wigfield, A., Metsala, J. L., & Cox, K. E. (1999). Motivational and cognitive predictors of text comprehension and reading amount. Scientific Studies of Reading, 3(3), 231–256. https://doi.org/10.1207/s1532799xssr0303_3
Hendaryan, & Noviadi, A. (2023). The Role of Metacognition Strategies (Metacomprehension) and Inferential Ability in Improving Reading Comprehension Ability. KEMBARA: Jurnal Keilmuan Bahasa, Sastra, dan Pengajarannya, 9(2), 363–375. https://doi.org/10.22219/kembara.v9i2.26097
Ingrid Schoon, Samantha Parsons, Robert Rush, J. L. (2010). No title. Pediatrics, 3, e459–e466.
Islam, B., Ahmed, A., Islam, K., & Shamsuddin, A. K. (2014). Child education through animation: an experimental study. International Journal of Computer Graphics & Animation, 4(4), 43–52. https://doi.org/10.5121/ijcga.2014.4404
Juel, C. (1994). Learning to read and write in one elementary school. in Learning to Read and Write in One Elementary School. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4612-4282-6
Kaganer, B. E., Giordano, G. A., Brion, S., & Tortoriello, M. (2010). Media_tablets_for_mobile.
Lister, M., Dovey, J., Giddings, S., Kelly, K., & Grant, I. (2006). Women & media: a critical introduction. In Choice Reviews Online (Vol. 44, Issue 04). https://doi.org/10.5860/choice.44-1949
Martin-Beltrán, M., Tigert, J. M., Peercy, M. M., & Silverman, R. D. (2017). Using digital texts vs. paper texts to read together: Insights into engagement and mediation of literacy practices among linguistically diverse students. International Journal of Educational Research, 82, 135–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijer.2017.01.009
McLaughlin, M., & Fisher, D. (2012). Teaching students to meet the common core standards in grades 6-12? In Reading Today (Vol. 30, Issue 3).
Merryfield, M. M. (2009). The challenge of globalization: Preparing teachers for a global age. Tep Vol 21-N4, 434.
Miles, M. B., & Huberman, A. M. (2007). Analisis Data Kualitatif: Buku Sumber tentang Metode-Metode Baru. terjemahan Tjetjep Rohendi Rohidi. Jakarta: Universitas Indonesia Press.
Molina, A. I., Navarro, Ó., Ortega, M., & Lacruz, M. (2018). Evaluating multimedia learning materials in primary education using eye tracking. Computer Standards and Interfaces, 59(February), 45–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csi.2018.02.004
Morocco, C. C., Aguilar, C. M., Bershad, C., Kotula, A. W., & Hindin, A. (2012). Supported literacy for adolescents: transforming teaching and content learning for the twenty-first century. In Supported Literacy for Adolescents: Transforming Teaching and Content Learning for the Twenty-First Century. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781118269350
Muhammad, K. (2019). Kesulitan siswa sekolah dasar dalam meningkatkan kemampuan literasi. Jurnal Pendidikan Almuslim, VII(2), 94–102.
Musfiqon, H. M. (2012). Pengembangan media dan sumber pembelajaran. Jakarta: PT. Prestasi Pustakaraya.
Nurhadi, N. (2016). Strategi meningkatkan daya baca (N. Syamsiyah. Bumi Aksara.
Nuttall, C. (1996). Teaching reading skills in a foreign language. ERIC.
Paterson, L. (2009). Civic values and the subject matter of educational courses. Oxford Review of Education, 35(1), 81–98.
Pérez, A., Santamaria, E. K., Operario, D., Tarkang, E. E., Zotor, F. B., Cardoso, S. R. de S. N., Autor, S. E. U., De, I., Dos, A., Vendas, O. D. E., Empresas, D. A. S., Atividades, P. O., Artigo, N., Gest, G. N. R. M. D. E., Para, D. E. F., Miranda, S. F. da R., Ferreira, F. A. A., Oliver, J., Dario, M., … Volk, J. E. (2017). Culture, curriculum, and identity in education. In BMC Public Health (Vol. 5, Issue 1).
Polizzi, G. (2020). Digital literacy and the national curriculum for England: Learning from how the experts engage with and evaluate online content. Computers and Education, 152, 103859. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2020.103859
Prensky, M. R. (2010). Teaching digital natives: Partnering for real learning. Corwin press.
Rasiwan, R., Sasongko, H. W., Arif, R. M., Setiawan, R., Rabihati, E., & Supardi, I. (2023). Learning media development based on 3D (3D) animation videos in courses mechanics technique. International Research Journal of Engineering, IT and Scientific Research, 9(2), 47–56. https://doi.org/10.21744/irjeis.v9n2.2274
Riyanti, A. (2021). Keterampilan membaca. Penerbit K-Media.
Sahasrabudhe, V., & Kanungo, S. (2014). Appropriate media choice for e-learning effectiveness: Role of learning domain and learning style. Computers and Education, 76, 237–249. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2014.04.006
Samsiyah, N., Suwandi, S., & Suhita, R. (2022). Local culture animation design: explore the art of javanese dance. Journal of Positive School Psychology, 2022(5), 6940–6947.
Schunk, D. H. (2003). Self-efficacy for reading and writing: Influence of modeling, goal setting, and self-evaluation. Reading &Writing Quarterly, 19(2), 159–172. https://doi.org/10.1080/10573560308219
Setiawan, A. ., & Musaffak, M. (2021). Profil penelitian keterampilan membaca cepat pada jurnal pendidikan bahasa dan sastra Indonesia dalam PPJB-SIP. KEMBARA: Jurnal Keilmuan Bahasa, Sastra, dan Pengajarannya, 7(2), 463–475. https://doi.org/10.22219/kembara.v7i2.17889
Setiawan, A., Hang, N. T. T., Fauzan, F., & Derana, G. T. (2023). Critical reading research and its implications for critical reading skills for Indonesian language teachers: A systematic literature review. BAHASTRA, 43(2), 152-182. https://doi.org/10.26555/bs.v43i2.500
Stonebraker, P. W., & Hazeltine, J. E. (2004). Virtual learning effectiveness: An examination of the process. The Learning Organization, 11(3), 209–225. https://doi.org/10.1108/09696470410532987
Suwandi, S. (2015). Peran bahasa Indonesia dalam pengembangan budaya literasi untuk mewujudkan bangsa yang unggul dalam konteks masyarakat ekonomi ASEAN. Peran Bahasa Dan Sastra Indonesia Dalam Menghadapi Masyarakat Ekonomi Asean (MEA), November, 1–17.
https://doi.org/10.31227/osf.io/aqtwe
Syamsiyah, N. (2020). Pembelajaran daring masa pandemi corona (kegiatan belajar di rumah dalam group kelas 4 mi as-salam). IBTIDA’: Media Komunikasi Hasil Penelitian Pendidikan Guru Madrasah Ibtidaiyah, 01(02), 115–125. https://journal.stitaf.ac.id/index.php/ibtida
Tetriyani, E., Jihad, A., Rachmawati, T. K., & Sugilar, H. (2024). Development of video animation media for learning a system two-variable linear equation. KnE Social Sciences, 423–430.
https://doi.org/10.18502/kss.v9i8.15575
Thoman, E., & Jolls, T. (2005). Media literacy education: Lessons from the center for media literacy. Yearbook of the National Society for the Study of Education, 104(1), 180–205.
Wardani, S., & Endahati, N. (2019). Animasi media pembelajaran bermuatan kearifan lokal. Seri Prosiding Seminar Nasional Dinamika Informatika, 3(1).
Xiao, L. (2013). Animation trends in education. International Journal of Information and Education Technology, 3(3), 286.
Zuber‐Skenitt, O. (1993). Improving learning and teaching through action learning and action research. Higher Education Research and Development, 12(1), 45–58. https://doi.org/10.1080/0729436930120105
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with The KEMBARA: Jurnal Keilmuan Bahasa, Sastra, dan Pengajarannya (e-Journal) agree to the following terms:
Articles are published under the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY 3.0).
Under the CC-BY license, authors retain ownership of the copyright for their article, but authors grant others permission to use the content of publications in KEMBARA: Jurnal Keilmuan Bahasa, Sastra, dan Pengajarannya (e-Journal) in whole or in part provided that the original work is properly cited. Users (redistributors) of KEMBARA: Jurnal Keilmuan Bahasa, Sastra, dan Pengajarannya are required to cite the original source, including the author's names, KEMBARA: Jurnal Keilmuan Bahasa, Sastra, dan Pengajarannya (e-Journal) as the initial source of publication, year of publication, volume number and DOI (if available).
Authors may publish the manuscript in any other journal or medium but any such subsequent publication must include a notice that the manuscript was initially published by KEMBARA: Jurnal Keilmuan Bahasa, Sastra, dan Pengajarannya (e-Journal).
Authors grant KEMBARA: Jurnal Keilmuan Bahasa, Sastra, dan Pengajarannya (e-Journal) the right of first publication. Although authors remain the copyright owner, they grant the journal the irrevocable, nonexclusive rights to publish, reproduce, publicly distribute and display, and transmit their article or portions thereof in any manner.






_.png)
















