The influence of blended learning using the science technology society approach on learning independence
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.22219/raden.v4i1.32325Keywords:
blended learning, learning independence, online, science technology societyAbstract
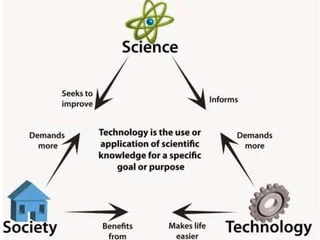
Independent learning facilitates students in improving their competencies according to the challenges of the current era. However, learning in schools often does not empower students to become independent learners. This research aims to find out whether the application of blended learning with the Science Technology Society (STS) approach can increase student independence in learning or not. This research is quantitative. The sample for this research was students from the informatics engineering and communication science study program at Dr Soetomo University. The instrument used in this research was a questionnaire. Questionnaires are used to find out information about independence. Data analysis involved conducting normality and homogeneity tests, followed by an independent sample test. The results of the analysis suggest an influence of blended learning with an STS approach on learning independence in higher education (t = 21.246, p < 0.001), implying the potential effectiveness of integrating STS principles into educational practices to foster greater autonomy among students.
Downloads
References
Ballouk, R., Mansour, V., Dalziel, B., McDonald, J., & Hegazi, I. (2022). Medical students’ self-regulation of learning in a blended learning environment: a systematic scoping review. Medical Education Online, 27(1). https://doi.org/10.1080/10872981.2022.2029336
Boyer, S. L., Edmondson, D. R., Artis, A. B., & Fleming, D. (2014). Self-directed learning: A tool for lifelong learning. Journal of Marketing Education, 36(1), 20–32. https://doi.org/10.1177/0273475313494010
Chen, L. (2022). Research on the cultivation of university students’ independent learning ability in the network environment. Advances in Educational Technology and Psychology, 6(11). https://doi.org/10.23977/aetp.2022.061114
Chervinska, I., Melnyk, N., & Galyuk, N. (2023). Blended learning as an innovative organization of the educational process in higher education institutions of Ukraine. Journal of Vasyl Stefanyk Precarpathian National University, 10(1), 216–224. https://doi.org/10.15330/jpnu.10.1.216-224
Collins, J. (2009). Lifelong learning in the 21st century and beyond. RadioGraphics, 29(2), 613–622. https://doi.org/10.1148/rg.292085179
Hansen, T. R., Marsango, D., & Santos, R. A. D. (2021). A presença da não neutralidade da ciência-tecnologia em literatura sobre a educação básica. Góndola, Enseñanza y Aprendizaje de Las Ciencias, 16(2). https://doi.org/10.14483/23464712.15823
Hoic-Bozic, N., Mornar, V., & Boticki, I. (2009). A blended learning approach to course design and implementation. IEEE Transactions on Education, 52(1), 19–30. https://doi.org/10.1109/TE.2007.914945
Jumini, S., Hidayah, R., & Hamzah, H. (2022). Science technology society (STS) learning through the utilization of potato skin waste on students’ science literacy. Radiasi : Jurnal Berkala Pendidikan Fisika, 15(2), 72–78. https://doi.org/10.37729/radiasi.v15i2.1828
Kárpáti, D. B., & Filep, J. C. (2023). Competences of students and expectations of employers regarding competencies in the training of teachers in economics. Acta Academiae Beregsasiensis. Economics, 3, 112–121. https://doi.org/10.58423/2786-6742/2023-3-112-121
Khompodoeva, M. V., Nikulina, L. P., & Shukaeva, A. V. (2020). Students’ independent cognitive activity and its formation at universities. In Integrating Engineering Education and Humanities for Global Intercultural Perspectives. IEEHGIP 2022. Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems (pp. 672–684). Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-47415-7_71
Knez, S., Podbregar, I., & Graham, N. (2022). Challenges and Development of Training in the Aviation Industry. Conference: 41st International Conference on Organizational Science Development: Society’s Challenges for Organizational Opportunities, March, 417–424. https://doi.org/10.18690/um.fov.3.2022.30
Krapivina, M. Y. (2023). Independent work of university students in learning a foreign language. Vestnik of Kostroma State University. Series: Pedagogy. Psychology. Sociokinetics, 28(3), 165–169. https://doi.org/10.34216/2073-1426-2022-28-3-165-169
Marope, P. T. M. (2014). Learning and competences for the 21st century. PROSPECTS, 44(4), 483–486. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11125-014-9333-y
Martínez, S., Guíñez, F., Zamora, R., Bustos, S., & Rodríguez, B. (2020). On the instructional model of a blended learning program for developing mathematical knowledge for teaching. ZDM, 52(5), 877–891. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11858-020-01152-y
Mastur, M. (2023). Blended learning strategy as a means of optimizing learning. Edukatif: Jurnal Ilmu Pendidikan, 5(1), 182–192. https://doi.org/10.31004/edukatif.v5i1.4715
Meganita, M., Papilaya, P. M., & Rumahlatu, D. (2022). Application of the science model community-based problem solving technology in improving learning outcomes, science process skills, and students scientific attitudes. BIOEDUPAT: Pattimura Journal of Biology and Learning, 2(1), 10–18. https://doi.org/10.30598/bioedupat.v2.i1.pp10-18
Mnisi, K. (2023). A case for deliberate and accommodative design for blended teaching and learning in universities in developing countries. Perspectives in Education, 41(2), 195–210. https://doi.org/10.38140/pie.v41i2.6863
Ntelok, Z. R. E., Resnasari, N. W. P., & Jamun, Y. M. (2022). Training students’ science literacy on biotechnology using science, environmental, technology, society (SETS) visioned learning instructional. Jurnal Basicedu, 6(3), 4925–4939. https://doi.org/10.31004/basicedu.v6i3.3002
Onah, D. F. O., Pang, E. L. L., & Sinclair, J. E. (2020). Cognitive optimism of distinctive initiatives to foster self-directed and self-regulated learning skills: A comparative analysis of conventional and blended-learning in undergraduate studies. Education and Information Technologies, 25(5), 4365–4380. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-020-10172-w
Özdemir, İ. H., Sarsar, F., & Harmon, S. W. (2023). Blended learning in higher education. In Handbook of Research on Current Trends in Cybersecurity and Educational Technology (pp. 365–389). IGI Global. https://doi.org/10.4018/978-1-6684-6092-4.ch020
Pashine, P. D. (2022). Blended learning: A need for change in education system. International Journal of Advanced Research in Science, Communication and Technology, 2(2), 76–79. https://doi.org/10.48175/IJARSCT-7418
Paudyal, G. R. (2022). Shift to technology-assisted learning through blended mode: University teachers’ experience. Prithvi Journal of Research and Innovation, 103–115. https://doi.org/10.3126/pjri.v4i1.50163
Rony, Z. T., Lubis, F. M., Yasin, M., & Soegiarto, I. (2022). The role of higher education leaders actualize independent learning program independent campus. Cypriot Journal of Educational Sciences, 17(12), 4683–4698. https://doi.org/10.18844/cjes.v17i12.8589
Salavatulina, L. R., Vorozheikina, A. V., Gnatyshina, E. V., Vasilenko, E. A., & Shabalina, A. A. (2022). Transformation of didactic space Of blended learning at university. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences, 539–544. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2022.11.74
Sugiyono, S. (2014). Metode penelitian kuantitatif, kualitatif, dan R&D. Alfabeta. https://opac.perpusnas.go.id/DetailOpac.aspx?id=911046
Wahyuni, E. (2018). Improving studentsr independence and collaboration with blended learning. Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Community Development (AMCA 2018). https://doi.org/10.2991/amca-18.2018.170
Wijanayu, A., Hardyanto, W., & Isnaeni, W. (2018). Blended learning method based on Quipper school to improve concepts understanding and independence learning. Journal of Primary Education, 7(1), 88–95. https://doi.org/10.15294/JPE.V7I1.22126
Wong, I. L. (2013). Developing independent learning skills for postgraduate students through blended learning environment. Journal of Cases on Information Technology, 15(1), 36–50. https://doi.org/10.4018/jcit.2013010103
Yoon, J., & Olsen, A. (2023). Promoting science affinities through a video project in a science, technology, and society (STS) learning approach. International Journal of Education in Mathematics, Science and Technology, 11(4), 1073–1093. https://doi.org/10.46328/ijemst.3049
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Nuril Huda, Windi Setiawan, H. Haerussaleh

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with Research and Development in Education agree to the following terms:
- For all articles published in the Research and Development in Education, copyright is retained by the authors. Authors give permission to the publisher to announce the work with conditions. When the manuscript is accepted for publication, the authors agree to the automatic transfer of non-exclusive publishing rights to the publisher.
- Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See The Effect of Open Access).

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.







