Teachers’ opinion about learning continuum in evolution based on the material complexity level
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.22219/jpbi.v7i1.13680Keywords:
Learning continuum, Complexity Level, EvolutionAbstract
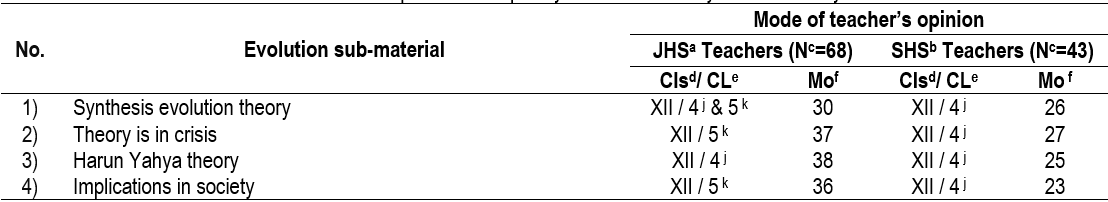
Evolution is one of biology topics which covers a wide range of material taught across education levels. Unfortunately, the material has not been arranged according to its complexity level and students’ development. This study aimed to collect teachers' opinions about the learning continuum of evolution material based on its complexity level. This descriptive research was conducted in Bantul and Yogyakarta Cities by distributing questionnaires. As many as 68 junior high school (JHS) teachers and 43 senior high schools (SHS) teachers were selected through convenience sampling. The data gained was analyzed using descriptive statistics to determine the mode of practitioner opinion. The results showed that the JHS teachers thought that evolutionary material had a complexity level of 3 (quite complex) to level 5 (very complicated) that could be taught in class VII & IX as well as at higher level (XII SHS). Furthermore, the SHS teachers argued that the evolution material from level 3 (quite complex) to level 4 (complex) could be taught in XII class. Further research needs to be carried out using more complete instruments with more detailed indicators.Downloads
References
Afidah, M. (2017). Identifikasi pola miskonsepsi mahasiswa pada konsep mekanisme evolusi menggunakan Certainty Of Response Index (CRI). Bio-Lectura: Jurnal Pendidikan Biologi, 4(2), 129–140. https://doi.org /10.31849/bl.v4i2.394
Agustina, A., & Ahmad, M. Y. (2020). A study on students’ cognitive development in answering english task. Al-Hikmah: Jurnal Agama Dan Ilmu Pengetahuan, 17(1), 11–28. https://doi.org/10.25299/al-hikmah:jaip .2020.vol17(1).3888
Andriani, A. E., & Subali, B. (2017). Teachers’ opinion about learning continuum based on student’s level of competence and specific pedagogical material in classification topics. AIP Conference Proceedings, 1868. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4995211
Asih, T. (2018). Perkembangan tingkat kognitif peserta didik di Kota Metro. Didaktika Biologi: Jurnal Penelitian Pendidikan Biologi, 2(1), 9–17. https://doi.org/10.32502/dikbio.v2i1.909
Awwad, A. A. A. (2013). Piaget’s theory of learning. Interdisciplinary Journal of Contemporary Research In Business, 4(9), 106–129. https://journal-archieves27.webs.com/106-129.pdf
Barrouillet, P. (2015). Theories of cognitive development: From Piaget to today. Developmental Review, 38, 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dr.2015.07.004
Bujuri, D. A. (2018). Analisis perkembangan kognitif anak usia dasar dan implikasinya dalam kegiatan belajar mengajar. LITERASI (Jurnal Ilmu Pendidikan), 9(1), 37. https://doi.org/10.21927/literasi.2018.9(1).37-50
Candramila, W., Adrianto, O. M., & Ariyati, E. (2016). Pemahaman konsep evolusi di Perguruan Tinggi. Seminar Nasional Pendidikan dan Saintek 2016, May 2016, 878–886. https://publikasiilmiah.ums.ac.id/handle /11617/8026
Carey, S., Zaitchik, D., & Bascandziev, I. (2015). Theories of development: In dialog with Jean Piaget. Developmental Review, 38, 36–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dr.2015.07.003
Çimer, A. (2012). What makes biology learning difficult and effective: Students’ views. Educational Research and Reviews, 7(3), 61–71. https://doi.org/10.5897/ERR11.205
Darling-Hammond, L., & John Bransford. (2005). Preparing teachers for a changing world: What teachers should learn and be able to do. Jossey-Bass. https://doi.org/10.5860/choice.43-1083
Edgar, T. W., & Manz, D. O. (2017). Exploratory Study. In Research Methods for Cyber Security (pp. 95–130). https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-12-805349-2.00004-2
Hadi, R. F., & Subali, B. (2017). The learning continuum based on student’s level of competence and specific pedagogical learning material on physiological aspects from teachers’s opinions. AIP Conference Proceedings, 1868. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4995216
Hanurani, H. (2019). Gambaran umum penguasaan materi ujian nasional tingkat SMA/MA mata pelajaran Biologi. JPPS (Jurnal Penelitian Pendidikan Sains), 9(1), 1735–1739. https://journal.unesa.ac.id/index. php/jpps/article/view/5448
Helmi, T., Rustaman, N., Tapilouw, F., & Hidayat, T. (2019). Perspektif ilmiah dan keyakinan terhadap evolusi mahasiswa biologi di universitas berbasis agama. Jurnal Sosial Humaniora, 10(2), 83. https://doi.org/10.30997/jsh.v10i2.1874
Hikmawati, N. (2018). Analisa kesiapan kognitif siswa SD/MI. Kariman, 6(1), 109–128. http://download. garuda.ristekdikti.go.id/article.php?article=528577&val=10827&title=analisa kesiapan kognitif siswa sdmi.
Ibda, F. (2015). Perkembangan kognitif: Teori Jean Piaget. Intelektualita, 3(1), 242904. https://www.jurnal.ar-raniry.ac.id/index.php/intel/article/view/197
Jirana, J., & Amin, M. (2016). Persepsi dosen dan mahasiswa terhadap buku ajar dan metode pembelajaran yang digunakan dalam membelajarkan calon guru biologi. Prosiding Seminar Nasional II 2016, Kerjasama Prodi Pendidikan Biologi FKIP Dengan Pusat Studi Lingkungan Dan Kependudukan (PSLK) Universitas Muhammadiyah Malang, 1, 1019–1028. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/319945026
Juniati, E., & Subali, B. (2017). Teacher’s opinion about learning continuum of genetics based on student’s level of competence. AIP Conference Proceedings, 100002. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4995212
Juwantara, R. A. (2019). Analisis teori perkembangan kognitif Piaget pada tahap anak usia operasional konkret 7-12 tahun dalam pembelajaran Matematika. Al-Adzka: Jurnal Ilmiah Pendidikan Guru Madrasah Ibtidaiyah, 9(1), 27. https://doi.org/10.18592/aladzkapgmi.v9i1.3011
Kose, U., & Arslan, A. (2017). Realizing an optimization approach inspired from Piaget’s theory on cognitive development. Broad Research in Artificial Intelligence and Neuroscience, 6(1–4), 15–22. https://arxiv.org/ftp/arxiv/papers/1704/1704.05904.pdf
Kusumadewi, M. ., Subali, B., & Paidi. (2019). Developing a learning continuum of biological resources management aspect from elementary school to senior high school based on the experts’ opinions. Journal of Physics: Conference Series., 1397. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1397/1/012052
Kusumawati, M. U., Subali, B., & Paidi. (2019). Developing a learning continuum of biological resources management aspect from Elementary School to Senior High School based on the experts’ opinions. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 1397(1). https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1397/1/012052
Lemos, M. S., & Veríssimo, L. (2014). The relationships between intrinsic motivation, extrinsic motivation, and achievement, along elementary school. Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences, 112, 930–938. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2014.01.1251
Liu, Z. (2016). Inspirations of relevance and spiral curriculum theory for EGP teaching. IOSR Journal of Research & Method in Education, 6(5), 62–65. https://doi.org/10.9790/7388-0605046265
Mattsson, J.-E., & Mutvei, A. (2015). How to Teach Evolution. Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences, 167, 170–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2014.12.658
Mauliya, A. (2019). Perkembangan Kognitif pada Peserta Didik SMP (Sekolah Menengah Pertama) Menurut Jean Piaget. ScienceEdu, II(2), 86. https://doi.org/10.19184/se.v2i2.15059
McNeill, M., Gosper, M., & Xu, J. (2012). Assessment choices to target higher order learning outcomes: The power of academic empowerment. Research in Learning Technology, 20(3), 283–296. https://doi.org /10.3402/rlt.v20i0.17595
Mendala, Subali, B., & Paidi. (2019). Developing a learning continuum on ecological aspect from elementary to senior high school based on the opinions of biology education experts. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 1397(1). https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1397/1/012053
Nurhadi. (2020). Teori kognitivisme serta aplikasinya dalam pembelajaran. Jurnal Edisi, 2(1), 77–95. https://doi.org/10.36088/edisi.v2i1.786
Nurjan, S. (2016). Psikologi belajar. Wade Group. http://eprints.umpo.ac.id/4909/1/Buku Psikologi Belajar.pdf
Pramesti, I. C., & Subali, B. (2017). The learning continuum of ecology based on teachers’ opinion about student’s level of competence and specific pedagogical learning material. AIP Conference Proceedings, 1868. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4995213
Prihatni, Y., Kumaidi, K., & Mundilarto, M. (2016). Pengembangan instrumen diagnostik kognitif pada mata pelajaran IPA di SMP. Jurnal Penelitian Dan Evaluasi Pendidikan, 20(1), 111–125. https://doi.org/10. 21831/pep.v20i1.7524
Priyayi, D. F., Keliat, N. R., & Hastuti, S. P. (2018). Masalah dalam pembelajaran menurut perspektif guru biologi sekolah menengah Atas (SMA) di Salatiga dan Kabupaten Semarang. Jurnal Penelitian Pendidikan Biologi, 2(2), 85–92. https://doi.org/10.32502/dikbio.v2i2.1243
Saputra, A. (2017). Persepsi mahasiswa calon guru biologi tentang pembelajaran materi evolusi di SMA: Studi kasus mahasiswa Pendidikan Biologi FKIP Universitas Sebelas Maret Surakarta. Bioeducation Journal, 1(1), 1–9. http://ejournal.unp.ac.id/index.php/bioeducation/article/view/7085
Sidiq, Y. (2016). Evolusi dalam kehidupan sehari-hari: Sudut pandang mahasiswa terhadap evolusi. Proceeding Biology Education ConferenceProceeding Biology Education Conference, 13(1), 583–586. https://jurnal. uns.ac.id/prosbi/article/view/5840
Simatwa, E. M. W. (2010). Piaget’s theory of intellectual development and its implication for instructional management at presecondary school level. Educational Research and Reviews, 5(7), 366–371. https:// eric.ed.gov/?id=EJ898837
Situmorang, R. P. (2016). Analisis learning continuum tingkat SD sampai SMP pada tema sistem pencernaan manusia. Scholaria: Jurnal Pendidikan dan Kebudayaan, 6(2), 1. https://doi.org/10.24246/j.scholaria. 2016.v6.i2.p1-13
Subali, B., Kumaidi, K., & Aminah, N. S. (2018). Developing a scientific learning continuum of natural science subjects at grades 1 - 4. Journal of Turkish Science Education, 15(2), 66–81. https://doi.org/10. 12973/tused.10231a
Suryanda, A., Azrai, E. P., & Julita, A. (2020). Analisis kebutuhan pengembangan buku saku biologi berbasis mind map (Biomap). Jurnal Pendidikan Matematika dan IPA, 11(1), 86–98. https://doi.org/ 10.26418/jpmipa.v11i1.31861
Suyanto, S. (2018). The implementation of the scientific approach through 5MS of the revised curriculum 2013 in Indonesia. Cakrawala Pendidikan, 37(1), 1689–1699. https://doi.org/10.21831/cp.v37i1.18719
Sztajn, P., Confrey, J., Wilson, P. H., & Edgington, C. (2012). Learning trajectory based instruction toward a theory of teaching. Educational Researcher, 41(5), 147–156. https://doi.org/10.3102/0013189X12442801
Taufik, L. M. (2019). Teori evolusi Darwin: Dulu, kini dan nanti. Jurnal Filsafat Indonesia, 2(3), 98–102. https://doi.org/10.23887/jfi.v2i3.22150
Trilipi, D., & Subali, B. (2020). The learning continuum of living reproduction: Generating a curriculum grid based on students’ cognitive levels. JPBI (Jurnal Pendidikan Biologi Indonesia), 6(3), 389–396. https://doi.org/10.22219/jpbi.v6i3.13660
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2021 Faridah & Subali

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with JPBI (Jurnal Pendidikan Biologi Indonesia) agree to the following terms:
- For all articles published in JPBI, copyright is retained by the authors. Authors give permission to the publisher to announce the work with conditions. When the manuscript is accepted for publication, the authors agree to automatic transfer of the publishing right to the publisher.
- Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See The Effect of Open Access).

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.

















