Content analysis of cell division concepts in Senior High School Biology textbooks
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.22219/jpbi.v8i2.18545Keywords:
Cell cycle, Cell division, Content analysis, Senior High School Biology textbooksAbstract
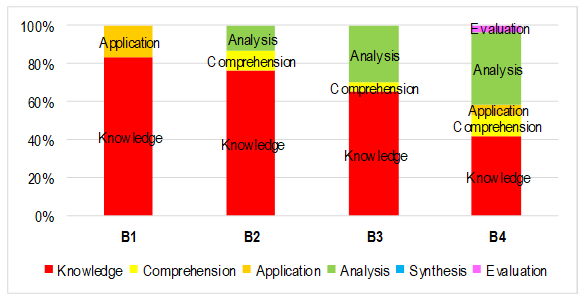
Content and accuracy evaluation of textbooks is important as it provides quality assurance to both teachers and learners, especially in the new normal where modular instruction is used. This research aimed at evaluating the biology textbooks used by Senior High School STEM Science teachers (n=15) in content, presentation, and learning strategies. Content analysis and Collaizzi’s descriptive phenomenology approach were employed in this study. The results showed that all evaluated textbooks have unique, distinct content, presentation, and learning strategies. Most topics were also aligned with the minimum curriculum requirement for SHS STEM, but topics such as cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs) and control checkpoints were not discussed in some books. Learning outcomes were not indicated in some books, and few textbooks did not reach synthesis and evaluation level. However, a comparative approach of cell division across the 5-kingdom system is observed but not explained well, and some misleading statements in the cell division mechanism were present. Considering that cell division precedes the discussion of cancer cell division and metastasis, content enrichment through learner-friendly visuals and diagrams is recommended to facilitate learning, improve retention, and avoid misconceptions.
Downloads
References
Altbach, P. G., & Kelly, G. P. (1998). Textbooks in the third world: Policy, content and context. New York: Garland Publishing. Retrieved from: https://eric.ed.gov/?id=ED419725
Ambag, R. (2018). Teaching Science in the Philippines: Why (and how) we can do better. Retrieved from: https://www.flipscience.ph/news/features-news/features/teaching-science-philippines/
Atilla, C. I. (2012). What makes biology learning difficult and effective: Students views. Educational research and reviews, 7(3), 61-71. https://doi.org/10.5897/ERR11.205
Bansiong, A. J., & Wan, P. (2019). Readability, Content, and Mechanical Feature Analysis of selected Commercial Science Textbooks Intended for Third Grade Filipino Learners. Cogent Education, 6(1). https://doi.org/10.1080/2331186x.2019.1706395
Barnes, M., Clayborne, J., & Palmer, S. S. (2005). Book pricing: Publisher, vendor, and library perspectives. Collection Building. https://www.emerald.com/insight/content/doi/10.1108/0160495051 0608258/full/html
Barrus, J. (2018). How to accurately summarize chapters. The Classroom. https://www.theclassroom.com/ accurately-summarize-chapters-8561101.html
Beidler, P. (2006). Optimized typesetting by read how you want. http://www.peytonstafford.com/ images/ReadHowYouWant_White_Paper.pdf
Behnke, Y. (2018). Textbook effects and efficacy. In the Palgrave handbook of textbook studies, 383–398. https://doi.org/10.1057/978-1-137-53142-1
Bernardo, A. S. (2013). English (es) in college English textbooks in the Philippines. US-China Foreign Language, 11(5), 355-380. http://www.davidpublisher.com/Public/uploads/Contribute/552f726c7 f599.pdf
Bhatti, A. J., Jumani, N. B., & Bilal, M. (2015). Analysis of alignment between curriculum and Biology textbook at Secondary Level in Punjab. Pakistan Journal of Social Sciences (PJSS), 35(1). http://pjss.bzu. edu.pk/index.php/pjss/article/view/306/276
Boone, P. T. (2010). Explicit instruction in United States history textbooks exercises: the role of exercises in navigating and critically evaluating textbooks. Scholar Works: Research & Innivations. http://hdl. handle.net/11714/4286
Bouma, H. (1980). Visual reading processes and the quality of text displays. In Grandjean, E., & Vigliani, E. (Eds.), Ergonomic aspects of visual display terminals: international workshop, 1980, Milan: proceedings, 101-114. Taylor and Francis Ltd. https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Visual-reading-processes-and-the-quality-of-text-Bouma/47b4c640791b44c33b67baeeb7dacb305f97ead7
Candra, P., Mercuriani, I. S., Nugroho, E. D., & Vlorensius, V. (2020). The biological content accuracy of natural Science textbooks for VIII Grade. JPBI (Jurnal Pendidikan Biologi Indonesia), 6(1), 135-146. https://doi.org/10.22219/jpbi.v6i1.10837
Cebrián, G., Junyent, M., & Mulà, I. (2020). Competencies in education for sustainable development: Emerging teaching and research developments. Sustainability, 12(2), 1–9. https://doi.org/10. 3390/su12020579
Chattopadhyay, A. (2012). Understanding of mitosis and meiosis in higher secondary students of Northeast India and the implications for genetics education. Scientific & Academic Publishing. https://doi.org/ 10.5923/j.edu.20120203.04
Clark, I. (2011). Formative assessment: policy, perspectives, and practice. Florida Journal of Educational Administration & Policy, 4, 158–180. Retrieved from: https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/EJ931151.pdf
Clerides, S. K. (2002). Book value: intertemporal pricing and quality discrimination in the US market for books. International Journal of Industrial Organization, 20(10), 1385-1408. https://doi.org/10.10 16/S0167-7187(02)00004-8
Clifford, P. (2002). The pressure-flow hypothesis of phloem transport: misconceptions in the A-level textbooks. Journal of Biological Education, 36 (3), 110–112. https://doi.org/10.1080/00219266.2002.9655814
Cook, M. (2008). Students’ comprehension of science concepts depicted in textbook illustrations. The Electronic Journal for Research in Science & Mathematics Education, 12(1). https://ejrsme.icrsme. com/article/view/7765
Dikenli, M. (2009). Conceptual problems in Biology-related topics in primary science and technology books in Turkey. International Journal of Environmental Science and Education, 4(4), 429-440. https://files. eric.ed.gov/fulltext/EJ884407.pdf
Dilber, R., & Duzgun, B. (2008). Effectiveness of analogy on students’ success and elimination of misconceptions. Latin American Physics Education, 2(3), 174-183, https://dialnet.unirioja.es/ descarga/articulo/2734605.pdf
Driscoll, M. P., Moallem, M., Dick, W., & Kirby, E. (1994). How does the textbook contribute to learning in a middle school science class? Contemporary educational psychology, 19(1), 79-100. https://doi.org/10.1006/ ceps.1994.1008
Duerr, L. (2008). Interdisciplinary instruction. Educational Horizons, 86(3), 173-180. http://www.jstor.org/stable/ 42923725
Dunlosky, J., Rawson, K. A., Marsh, E. J., Nathan, M. J., & Willingham, D. T. (2013). Improving students’ learning with effective learning techniques: Promising directions from cognitive and educational psychology. Psychological Science in the Public Interest, 14(1), 4–58. https://doi.org/10.1177/ 1529100612453266
Education Bureau the Government of the Hong Kong Administrative Region. (2016). Guiding Principles for Quality Textbooks (Revised June 2016). https://www.edb.gov.hk/en/curriculum-development/resource-support/textbook-info/GuidingPrinciples/index.html
Fan, L. (2010). Principles and processes for publishing textbooks and alignment with standards: A case in Singapore. APEC Conference on Replicating Exemplary Practices in Mathematics Education, Koh Samui, Thailand, 7‐12 Mar. 2010 [APEC#210‐HR‐01.4] https://www.apec.org/docs/default-source/Publications/2010/7/Replicating-Exemplary-Practices-in-Mathematics-Education-among-APEC-Economies-July-2010/TOC/Lianghuo-Fan-Principles-and-Processed-for-Publishing-Textbooks-and-Alignment-with-Standards-A-Case-i.pdf
Florida Department of Education. (2008). Priorities for evaluating instructional materials: A research update. Florida University Department of Education. http://realm.cimes.fsu.edu/resources/files/research Reportfinal.pdf.
Functional Literacy, Education and Mass Media Survey (FLEMMS). (2020). Philippine statistics authority. Reference Number: 2020-406. https://psa.gov.ph/content/functional-literacy-rate-estimated-916-percent-2019
Functional Literacy, Education and Mass Media Survey (FLEMMS). (2019). Philippine statistics authority. Reference Number: 2020-406. https://psa.gov.ph/content/functional-literacy-rate-estimated-916-percent-2019 Date accessed: December 11, 2020.
Functional Literacy, Education and Mass Media Survey (FLEMMS). (2016). Philippine statistics authority. Reference Number: 2020-406. https://psa.gov.ph/content/functional-literacy-rate-estimated-916-percent-2019
Gamble, T. K., & Gamble, M. W. (2013). Interpersonal communication: Building connections together. Sage Publications. ISBN 978-1-4522-2013-0
Geske, J. (1996). Legibility of sans serif type for use as body copy in computer mediated communication. Presented at Annual Meeting of the Association for Education in Journalism and Mass Communication 1996. https://eric.ed.gov/?id=ED399590
Gök, T. I. (2012). Comparative analysis of Biology textbooks with regard to cellular respiration and photosynthesis. Doctoral dissertation, Bilkent University. http://www.thesis.bilkent.edu.tr/0006040.pdf
Gu, X., Wu, B., & Xu, X. (2015). Design, development, and learning in e-textbooks: What we learned and where we are going. Journal of Computers in Education, 2(1), 25–41. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40692-014-0023-9
Hibbing, A. N., & Rankin-Erickson, J. L. (2003). A picture is worth a thousand words: using visual images to improve comprehension for middle school struggling readers. The Reading Teacher, 56(8), 758-770. https://go.gale.com/ps/i.do?id=GALE%7CA101762236&sid=googleScholar&v=2.1&it=r&linkaccess=abs&issn=00340561&p=AONE&sw=w&userGroupName=anon%7E651082ac
International Standard Classification of Education (ISCED). (2012). United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization, Institute for Statistics. ISBN 978-92-9189-123-8.
Irez, S. (2016). Representations of the nature of scientific knowledge in Turkish Biology textbooks. Journal of Education and Training Studies, 4(7), 196-210. https://doi.org/10.11114/jets.v4i7.1507
Juwita, A. N., Budiwati, R., & Ambarwati, L. (2017). An analysis on cohesion within sophomore students’ essay writings. In The 5th Undergraduate Conference on ELT, Linguistics, and Literature 2017, 29. Sanata Dharma University Press. https://sshraweb.org/wp-content/uploads/2018/07/SSHRA-ICBELLP-International-Conference-Bali-July-2017.pdf
Khalil, M. K., & Elkhider, I. A. (2016). Applying learning theories and instructional design models for effective instruction. Advances in Physiology Education, 40(2), 147–156. https://doi.org/10.1152/advan. 00138.2015
Kashi, F., Andreeva, N., & Naeimi, A. (2015). The role of content analysis of Biology textbooks in process of their teaching and designing in Iran. Proceedings of International Academic Conferences 1003626, International Institute of Social and Economic Sciences. https://ideas.repec.org/p/sek/iacpro/ 1003626.html
Kasmaienezhadfard, S., Pourrajab, M., & Rabbani, M. (2015). Effects of pictures in textbooks on students’ creativity. Multi-Disciplinary Edu. Global Quest (Quarterly), 4(2), 83-96. ISSN 2250–3048. https://www. semanticscholar.org/paper/EFFECTS-OF-PICTURES-IN-TEXTBOOKS-ON-STUDENTS%27-Rabbani-Pourrajab/a3a9cb13eac1c5a25344a14dff1050c301f32fde
Khine, M. S. (2013a). Critical analysis of science textbooks: evaluating instructional effectiveness. Springer. ISBN 978-94-007-4167-6, https://www.pedocs.de/volltexte/2015/11030/pdf/cepsj_2014_1_Slapnicar_ Rezension_KhineSwe_Critical_analysys.pdf
Khine, M. S. (2013b). Analysis of Science textbooks for instructional effectiveness. In critical analysis of science textbooks, 303-310. Springer, Dordrecht. https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-94-007-4168-3_15
Kim, J. Y., Choi, D. S., Sung, C. S., & Park, J. Y. (2018). The role of problem-solving ability on innovative behavior and opportunity recognition in university students. Journal of Open Innovation: Technology, Market, and Complexity. 4, 4 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40852-018-0085-4
Kline, M., & Demuth, K. (2010). Factors facilitating implicit learning: the case of the Sesotho passive. Language Acquisition, 17(4), 220-234. https://doi.org/10.1080/10489223.2010.509268
Kumandaş, B., Ateskan, A., & Lane, J. (2018). Misconceptions in Biology: a meta-synthesis study of research. Journal of Biological Education, 2000–2014, 1-15, https://doi.org/10.1080/00219266.2018.1490798
Leivas Pozzer, L., & Roth, W. M. (2003). Prevalence, function, and structure of photographs in High School Biology textbooks. Journal of Research in Science Teaching, 40(10), 1089-1114. https://doi.org/ 10.1002/tea.10122
Lemmer, M., Edwars, J. A., & Rapule, S. (2008). Educators’ selection and evaluation of natural Sciences textbooks. South African Journal of Education, 28(2), 175-188. https://doi.org/10.15700/saje.v28n2 a169
Lent, R. C. (2012). Overcoming textbook fatigue: 21st century tools to revitalize teaching and learning. Ascd. ISBN 978-1-4166-1472.
Leonard, M.J., Kalinowski, S.T., & Andrews, T. C. (2014). Misconceptions yesterday, today, and tomorrow. CBE Life Sci Educ. 2014 Summer; 13(2), 179–186. https://doi.org/10.1187/cbe.13-12-0244
Liang, Y., & Cobern, W. W. (2013). Analysis of a typical Chinese high school biology textbook using the AAAS textbook standards. EURASIA Journal of Mathematics, Science and Technology Education, 9(4), 329-336. https://doi.org/10.12973/eurasia.2013.942a
Lubis, S. S., & Sahyar, S. (2021). The development of High School Physics textbooks based on Batak culture. In Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 1811(1), 012081. IOP Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1088/ 1742-6596/1811/1/012081
Lu, Q., & Liu, E. S. (2012). Research on the consistency of Biology textbooks for Senior High Schools with the curriculum standards—Taking the textbooks of People’s Education Press and Zhejiang Science and Technology Press as an Example. Curriculum, Teaching Material and Method, 32(5), 75-82. https:// caod.oriprobe.com/articles/29970209/Research_on_the_Consistence_of_Biology_Textbooks_f.htm
Luo, H. (2018). Passive voice usage in undergraduate STEM textbooks. Electronic Theses and Dissertations, 2004-2019. 5894. https://stars.library.ucf.edu/etd/5894/
Macasawang, E. M. A., Guimba, W. D., & Alico, J. C. (2019). Analysis on an English Textbook for Grade 7: Focus on Compliance to the K-12 Grade Level Standards and Competencies. Education Quarterly Reviews, 2(1), 41-51. https://doi.org/10.31014/aior.1993.02.01.37
Mahajan, M., & Singh, M. K. (2017). Importance and benefits of learning outcomes. IOSR Journal of Humanities and Social Science, 22(03), 65-67. https://doi.org/10.9790/0837-2203056567
Mariani, D. & Usmeldi. (2019). Needs analysis in the development of natural science student books connected type integrated of local cultural wisdom. In Journal of Physics: Conference Series. https://doi.org/10. 1088/1742-6596/1185/1/012071
Mathai, S. (2014). The role of science textbooks in influencing pedagogical practices: implications for teacher education. In Focus 2.0.
McCarthy, M. S., & Mothersbaugh, D. L. (2002). Effects of typographic factors in advertising-based persuasion: a general model and initial empirical tests. Psychology & Marketing, 19(7-8), 663-691. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/mar.10030
Mitchell, C. E., & Miller, L. D. (1995). Tech prep academics: Using real life connections to develop scientific and mathematical literacy. School Science and Mathematics, 95(8), 417-422. https://doi.org/ 10.1111/j.1949-8594.1995.tb10195.x
Morales, R., & Baker, A. (2018). Secondary students’ perceptions of open science textbooks. Journal of Interactive Media in Education, 1, 1–9. https://doi.org/10.5334/jime.455
Muslich, M. (2010). Text book writing: Dasar-dasar pemahaman, penulisan, dan pemakaian buku teks. Yogyakarta: Ar-Ruzz Media.
National Book Development Board (NBDB). (1995). Republic Act No. 8047 (Book Publishing Industry Development Act). https://booksphilippines.gov.ph/ra-8047/
Neilson, K. J. (2016). A text analysis of how passive voice in a biology textbook impacts English language learners. School of Education Student Capstone Theses and Dissertations. 4219. https://digital commons.hamline.edu/hse_all/4219
Nomoto, M., Nonaka, D., Mizoue, T., Kobayashi, J., & Jimba, M. (2011). Content analysis of school textbooks on health topics: A systematic review. Bioscience trends, 5(2), 61-68. https://doi.org/10.5582/ bst.2011.v5.2.61
Novitasari, C., Ramli, M., & Karyanto, P. (2019). Content analysis of misconceptions on bacteria in the biology textbook of high school. In Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 1157(2), 022076. IOP Publishing, https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1157/2/022076
Nugroho, E. D., Vlorensius, V., Rasidah, L. H., & Anisa, N. (2017). The content analysis, material presentation, and readability of curriculum 2013 Science textbook for 1st Semester of Junior High School 7th Grade. JPBI (Jurnal Pendidikan Biologi Indonesia), 3(2), 114-122, https://doi.org/ 10.22219/jpbi.v3i2.3904.
Oakes, J., & Saunders, M. (2002). Access to textbooks, instructional materials, equipment, and technology: Inadequacy and inequality in California’s public schools. Los Angeles; University of California. Williams Watch Series: Investigating the, Claims of Williams v. State of California.
OECD. (2018). PISA 2018 results. Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development. https://www.oecd.org/pisa/publications/pisa-2018-results.htm
Office of the President of the Philippines. (1999). Executive Order No. 119 Adoption of The National Book Policy. https://www.officialgazette.gov.ph/1999/07/04/executive-order-no-119-s-1999/
Okabe, M. (2013). Where does Philippine education go? The “K to 12” program and reform of Philippine basic education. IDE Discussion Papers 425, Institute of Developing Economies, Japan External Trade Organization (JETRO). https://core.ac.uk/download/pdf/288456571.pdf
Öztap, H., Özay, E., & Öztap, F. (2003). Teaching cell division to Secondary school students: an investigation of difficulties experienced by Turkish teachers. Journal of Biological Education, 38(1), 13-15. https:// doi.org/10.1080/00219266.2003.9655890
Park, M., Park, D. Y., & Lee, R. E. (2009). A comparative analysis of earth Science curriculum using inquiry methodology between Korean and the US textbooks. Eurasia Journal of Mathematics, Science and Technology Education, 5(4), 395-411. https://doi.org/10.12973/ejmste/75289
Poulton, E. C. (1959). Effects of printing types and formats on the comprehension of scientific journals. Nature, 184, 1824–1825. https://doi.org/10.1038/1841824a0
Rahmiwati, S., Ratnawulan, R., & Yohandri, Y. (2018). The implementation of integrated natural science textbook of junior high school be charged on character-based shared models to improve the competence of learners’ knowledge. In IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, 1–7. https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899X/335/1/012076
Rakes, G. C., Rakes, T. A., & Smith, L. J. (1995). Using visuals to enhance secondary students' reading comprehension of expository texts. Journal of Adolescent & Adult Literacy, 39(1), 46-54. https://www. jstor.org/stable/40016720
Reynolds, J. A., Thaiss, C., Katkin, W., & Thompson, R. J. (2012). Writing-to-learn in undergraduate science education: A community-based, conceptually driven approach. CBE Life Sciences Education, 11(1), 17–25. https://doi.org/10.1187/cbe.11-08-0064
Rogayan, Jr. D., & Albino, M. (2019). Filipino students' common misconceptions in Biology: Input for Remedial Teaching. 4, 90-103. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/337683279_Filipino_Students'_ Common_Misconceptions_in_Biology_Input_for_Remedial_Teaching
Ruhiat, Y., Hidayat, S., Suparno, H. A., & Wibowo, F. C. (2016). Teaching materials development based on basic competence through diffusion adaptation strategy to improve learning process of physics. PEOPLE: International Journal of Social Sciences, 2(1), 137–149. https://doi.org/10.20319/pijss.2016. s21.137149
Sainani, K., Elliott, C., & Harwell, D. (2015). Active vs. passive voice in scientific writing. [Webinar]. American Chemical Society. https://www.internationalscienceediting.com/active-versus-passive-voice-in-scientifi c-writing-infographic/
Shah, S. F. (2012). An investigation into the alignment between the government’s dictated English language curriculum and the textbook mediated classroom practice at the secondary level in Pakistan. A Master of Philosophy thesis at Nottingham Trent University. http://irep.ntu.ac.uk/view/creators/Shah=3ASF =3A=3A.html
Sidek, H. M. (2012). EFL textbook analysis: A case study. Language and Literacy, 14(3), 27–45. https://doi.org/10.20360/G2HP4J
Subbaram, V. M. (2004). Effect of display and text parameters on reading performance (Doctoral dissertation). OhioLINK Electronic Theses and Dissertations Center. http://rave.ohiolink.edu/etdc/view?acc_num= osu1089408221
Swanepoel, S. (2010). The assessment of the quality of science education textbooks: conceptual framework and instruments for analysis. Thesis. Institutional Repository, University of South Africa. http://hdl. handle.net/10500/4041
Tarasov, D. A., Sergeev, A. P., & Filimonov, V. V. (2015). Legibility of textbooks: a literature review. Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences, 174, 1300-1308. https://doi.org/ 10.1016/j.sbspro.2015.01.751
Tok, H. (2010). TEFL textbook evaluation: from teachers’ perspectives. Educational Research and Review, 5(9), 508-517. http://academicjournals.org/article/article1379623669_Hidayet.pdf
Townsend, L. A. (2012). The effects of laboratory-based activities on student attitudes toward science. Master’s Thesis, Montana State University, Bozeman, Montana.
World Economic Forum. (2018). The Global Competitiveness Report 2017–2018. Geneva: World Economic Forum. https://www3.weforum.org/docs/GCR2017-2018/05FullReport/TheGlobalCompetitivenessRepo rt2017%E2%80%932018.pdf
Yager, R. E. (1983). The importance of terminology in teaching K‐12 Science. Journal of Research in Science Teaching, 20(6), 577-588. https://doi.org/10.1002/tea.3660200610
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with JPBI (Jurnal Pendidikan Biologi Indonesia) agree to the following terms:
- For all articles published in JPBI, copyright is retained by the authors. Authors give permission to the publisher to announce the work with conditions. When the manuscript is accepted for publication, the authors agree to automatic transfer of the publishing right to the publisher.
- Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See The Effect of Open Access).

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.

















