Students’ scientific reasoning skills through RICOSRE model in environmental changes topic
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.22219/jpbi.v9i3.29308Keywords:
Environmental change topic, Problem learning model, RICOSRE, Scientific Reasoning SkillsAbstract
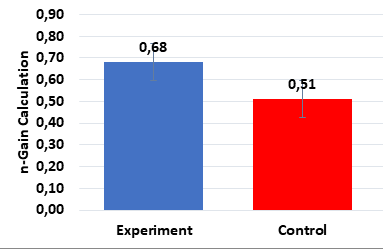
The low level of students' scientific reasoning skills is caused by the low-quality learning process. Action is needed to improve the learning process by applying innovative learning models, the Reading, Identification, Constructing, Solving, Reviewing, and Extending (RICOSRE) learning model. This research aims to determine the effect of RICOSRE Learning Model on Students' Scientific Reasoning Skills on the Topic of Environmental Changes of Class X MAN 1 Medan. This research uses a quasi-experiment with Non-equivalent Control Group Design. The population of this study is all class X Science and Technology MAN 1 Medan. The sample consisted of class X Science and Technology 1 with the RICOSRE learning model and X Science and Technology 2 with the conventional learning model. The results of the research show that the average pre-test and post-test data for scientific reasoning skills in the experimental class are 35.65 and 79.14, moreover in the control group are 33.94 and 67.76. Data was analyzed using an Independent Sample t-test using SPSS Version 26. Based on the t-test calculation at α = 0.05, a significance of 0.000 is obtained, which means there is an effect of the RICOSRE model on the scientific reasoning skills of students on environmental change topics.
Downloads
References
Adriani, M., Rahmat, A., & Hidayat, T. (2015). Kemampuan penalaran siswa SMA pada pembelajaran klasifikasi tumbuhan dengan dan tanpa praktikum virtual. Seminar Nasional XII Pendidikan Biologi FKIP UNS. November, 281–284.
Akın, F., Koray, Ö., & Tavukçu, K. (2015). How effective is critical reading in the understanding of scientific texts? Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences, 174, 2444–2451. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2015.01.915
Angga, A., Abidin, Y., & Iskandar, S. (2022). Penerapan pendidikan karakter dengan model pembelajaran berbasis keterampilan abad 21. Jurnal Basicedu, 6(1), 1046–1054. https://doi.org/10.31004/basicedu.v6i1.2084
Asry, L. (2020). Hubungan ilmu pengetahuan dan teknologi. Jurnal Biram Samtani Sains, 4(1), 40–50.
Bayazit, I. (2013). An investigation of problem-solving approaches, strategies, and models used by the 7th and 8th grade students when solving real-world problems. Kuram ve Uygulamada Egitim Bilimleri, 13(3), 1920–1927. https://doi.org/10.12738/estp.2013.3.1419
Bebasari, M., Jamna, J., & Marsidi, S. (2022). 21 st Century Education. 4(1), 1–7.
Boholano, H. (2017). Smart social networking: 21st Century teaching and learning skills. Research in Pedagogy, 7(2), 21–29. https://doi.org/10.17810/2015.45
Bulus, M. (2021). Sample size determination and optimal design of randomized/non-equivalent pretest-posttest control-group designs. Adıyaman Üniversitesi Eğitim Bilimleri Dergisi, 11(1), 48–69. https://doi.org/10.17984/adyuebd.941434
Cer, E., & Sahin, E. (2016). The effects of quality books for children and the metacognitive strategy on students’ self-esteem levels. Journal of Education and Learning, 6(1), 72. https://doi.org/10.5539/jel.v6n1p72
Diyah, M. (2018). Mengembangkan literasi informasi melalui belajar berbasis kehidupan terintegrasi PBL untuk menyiapkan calon pendidik dalam menghadapi era revolusi industri 4.0. ELEMENTARY: Islamic Teacher Journal, 6(5), 1–2. https://doi.org/10 .21831/cp.v1i1.4145
González, J., & Castillo, R.G. (2022). Reconfiguraciones espaciales y sociodemográficas de las migra-ciones chiapanecas aEstados Unidos (2009-2016) [Spatial and sociodemographic reconfigurations of the Chiapaneca migrations to the United State. Estudios Fronterizos, 23, 1–27.https://doi.org/10.21670/ref.2212096
Handayani, G., Windyariani, S., & Pauzi, R. (2020). Profil tingkat penalaran ilmiah siswa sekolah menengah atas pada materi ekosistem. BIODIK, 6, 71–81. https://doi.org/10.22437/bio. v6i2.9411
Hayati, N., Berlianti, N.A. (2020). Critical thinking skills of natural science undergraduate students on biology subject : Gender perspective. JPBI (Jurnal Pendidikan Biologi Indonesia), 6(1), 83–90.
Huang, S.-Y., Kuo, Y.-H., & Chen, H.-C. (2020). Applying Digital escape rooms infused with science teaching in elementary school: learning performance, learning motivation, and problem-solving ability. Thinking Skills and Creativity, 37, 100681. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsc. 2020.100681
Hulaikah, M., Degeng, I.N.S., Sulton, & Murwani, F.D. (2020). The effect of experiential learning and adversity quotient on problem solving ability. International Journal of Instruction, 13(1), 869–884. https://doi.org/10.29333/iji.2020.13156a
Joynes, C., Rossignoli, S., & Amonoo-Kuofi, E.F. (2019). 21st century skills: Evidence of issues in definition, demand and delivery for development contexts. (K4D Helpdesk Report), August,1–75. https://opendocs.ids.ac.uk/opendocs/handle/20.500.12413/14674
Mahanal, S., & Zubaidah, S. (2017). Model pembelajaran Ricosre yang berpotensi memberdayakan keterampilan berpikir kreatif. Jurnal Pendidikan, 2(5), 676–685. https://journal.um.ac. id/index.php/jptpp/
Mahanal, S., Zubaidah, S., Sumiati, I.D., Sari, T.M., & Ismirawati, N. (2019). RICOSRE: A learning model to develop critical thinking skills for students with different academic abilities. International Journal of Instruction, 12(2), 417–434. https://doi.org/10.29333/iji.2019.12227
Markowitz, D. M., Laha, R., Perone, B. P., Pea, R. D., & Bailenson, J.N. (2018). Immersive virtual reality field trips facilitate learning about climate change. In Frontiers in Psychology (Vol. 9). Frontiers Media S.A. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2018.02364
Maskur, R., Sumarno., Rahmawati, Y., Pradana, K., Syazali, M., Septian, A., & Kinarya, E. (2020). The effectiveness of problem based learning and aptitude treatment interaction in improving mathematical creative thinking skills on curriculum 2013. European Journal of Educational Research, 9(1), 375–383. https://doi.org/10.12973/eu-jer.9.1.375
Mawaddah, K., Mahanal, S., Gofur, A., Setiawan, D., & Zubaidah, S. (2021). RICOSRE: An innovative learning model to promote scientific literacy. AIP Conference Proceedings, 2330(March). https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0043303
Miftahurrohmah, U. U., Hariri, H., Rini, R., & Rohmatillah, R. (2021). Exemplary leadership practices in early childhood education in preparing the golden generations for Indonesia. Journal of Social, Humanity, and Education, 1(4), 253–268. https://doi.org/10.35912/jshe.v1i4.529
Mulnix, J. W. (2012). Thinking critically about critical thinking. Educational Philosophy and Theory, 44(5), 464–479. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-5812.2010.00673
Negley, H. (2022). Critical Thinking and Problem-Solving Skills. In The Salesforce Consultant’s Guide. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4842-7960-1_13
Novia, N., & Riandi, R. (2017). The analysis of students scientific reasoning ability in solving the modified lawson classroom test of scientific reasoning (MLCTSR) problems by applying the levels of inquiry. Jurnal Pendidikan IPA Indonesia, 6(1), 116–122. https://doi.org/ 10.15294/jpii.v6i1.9600
Rahman, M. M. (2019). 21st century skill “problem solving”: Defining the concept. Asian Journal of Interdisciplinary Research, 2(1), 71–81.
Riyadi, S.T.J., & Nikmaturrohmah, P. (2021). Profile of students’ problem-solving skillsviewed from Polya’s four-steps approach and elementary school students. European Journal of Educational Research, 10(4), 1625–1638. https://doi.org/10.12973/EU-JER.10.4.1625
Saxe, A., Nelli, S., & Summerfield, C. (2021). If deep learning is the answer, what is the question? Nature Reviews. Neuroscience, 22(1), 55–67. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41583-020-00395-8
Schleicher, A. (2018). The Future of Education and Skills: Education 2030. OECD Education Working Papers, 23.
Schoppe-Sullivan, S. J., & Fagan, J. (2020). The evolution of fathering research in the 21st century: persistent challenges, new directions. Journal of Marriage and Family, 82(1), 175–197. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1111/jomf.12645
Setiawan, D., Mahanal, S., & Zubaidah, S. (2021). RICOSRE: Effect and potential to enhance biology students’ digital literacy at Universitas Negeri Malang. In AIP Conference Proceedings (Vol. 2330). https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0043139
Simatupang, H., & Ionita, F. (2020). Pengaruh model problem based learning terhadap kemampuan pemecahan masalah materi pencemaran lingkungan siswa SMA Negeri 13 Medan. Jurnal Biolokus, 3(1), 245. https://doi.org/10.30821/biolokus.v3i1.680
Summaries, C. E. (2019). What Students Know and Can Do. PISA 2009 at a Glance, I. https://doi.org/10.1787/g222d18af-en
Suryanda, A., Azrai, E., & Wari, N. (2018). Pengaruh Penerapan model pembelajaran group investigation (GI) terhadap kemampuan berpikir analisis siswa pada materi pencemaran lingkungan. Biosfer: Jurnal Pendidikan Biologi, 9, 37–44. https://doi.org/10.21009/ biosferjpb.9-2.6
Suryanti, E., Fitriani, A., Redjeki, S., & Riandi, (2019). Identifikasi kesulitan mahasiswa dalam pembelajaran biologi molekuler berstrategi modified free inquiry (Identification of student difficulties in molecular biology with modified free inquiry learning strategy). Perspektif Pendidikan dan Keguruan, X(2).
Tanujaya, B., Mumu, J., & Margono, G. (2017). The relationship between higher order thinking skills and academic performance of student in mathematics instruction. International Education Studies, 10(11), 78. https://doi.org/10.5539/ies.v10n11p78
Temel, S. (2014). The effects of problem-based learning on pre-service teachers’ critical thinking dispositions and perceptions of problem-solving ability. South African Journal of Education, 34(1), 1–20. https://doi.org/10.15700/201412120936
Tivani, I., & Paidi, P. (2016). Pengembangan LKS biologi berbasis masalah untuk meningkatkan kemampuan pemecahan masalah dan karakter peduli lingkungan. Jurnal Inovasi Pendidikan IPA, 2(1), 35. https://doi.org/10.21831/jipi.v2i1.8804
Treffinger, D.J., & Isaksen, S.G. (2013). Teaching and applying creative problem solving: implications for at-risk students. International Journal for Talent Development and Creativity, 1(1), 87–97. https://eric.ed.gov/?id=EJ1301380
Ulger, K. (2018). The effect of problem-based learning on the creative thinking and critical thinking disposition of students in visual arts education. Interdisciplinary Journal of Problem-Based Learning, 12(1), 3–6. https://doi.org/10.7771/1541-5015.1649
Vebrian, R., Darmawijoyo, & Hartono, Y. (2016). Pengembangan SOAL MATEMATIKA TIPE TIMSS menggunakan konteks Kerajaan Sriwijaya di SMP. Jurnal Didaktik Matematika, 3(2), 96–105.
Yusup, I. R. (2018). Kesulitan guru pada pembelaran biologi tingkat madrasah/sekolah di provinsi Jawa Barat (Studi KASUS WILAYAH Priangan Timur). Jurnal Bioeduin : Program Studi Pendidikan Biologi, 8(2), 34–42. https://doi.org/10.15575/bioeduin.v8i2.3187
Widiantie, R.,& Lismaya, L. (2017). Upaya meningkatkan keterampilan pemecahan masalah dengan strategi ideal melalui pembelajaran berbasis masalah pada materi kelenjar endokrin. Journal Quagga, 9(1), 1–7.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with JPBI (Jurnal Pendidikan Biologi Indonesia) agree to the following terms:
- For all articles published in JPBI, copyright is retained by the authors. Authors give permission to the publisher to announce the work with conditions. When the manuscript is accepted for publication, the authors agree to automatic transfer of the publishing right to the publisher.
- Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See The Effect of Open Access).

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.

















